By Dr. Shantanu Mallick MBBS (Cal), DA (Mum), FIPP (UK), Pain Physician
It is not always clear why a patient develops shoulder complaints except it is due to trauma. In general, the pain  prevents the patient from sleeping on the affected side. The localization and radiation pattern of the pain can provide an indication as to whether one is dealing with a primary disease of the shoulder joint or with a cause external to the joint. Degenerative disease and overuses is the common, in shoulder pain along with some inflammatory diseases.
prevents the patient from sleeping on the affected side. The localization and radiation pattern of the pain can provide an indication as to whether one is dealing with a primary disease of the shoulder joint or with a cause external to the joint. Degenerative disease and overuses is the common, in shoulder pain along with some inflammatory diseases.
The shoulder is comprised of three bones: the humerus, scapula and calvicle. The shoulder is a very mobile joint and receives minimal stability from the bony structures. The soft tissue of the shoulder, including the rotator cuff muscles and joint capsule, function to help provide stability to the most mobile shoulder joint.
RISK FACTORS: 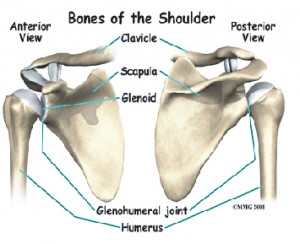
Cervical disk disease of the neck
Diabetes
Shoulder Injury
Shoulder Surgery
Open Heart Surgery
Hyperthyroidism
SYMPTOMS :
Decreased motion of the shoulder
Pain
Stiffness
Frozen shoulder without any known cause starts with pain. This pain prevents you from mo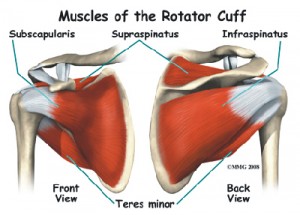 ving your arm. The lack of movement leads to stiffness and then even less motion. Over time, you become unable to perform activities such as reaching over your head or behind you.
ving your arm. The lack of movement leads to stiffness and then even less motion. Over time, you become unable to perform activities such as reaching over your head or behind you.
Diagnosis
Based on your symptoms and examination (movements restriction) of your shoulder, x-rays or MRI of the shoulder (as per requirement) will give the diagnosis.
Osteoarthritis of joint
Capsulitis of joint
Rotator cuff syndrome
Osteoarthritis of Acromio-clavicular joint
Impingement syndrome
Subacromial bursitis
Treatment
Conservative Treatment : 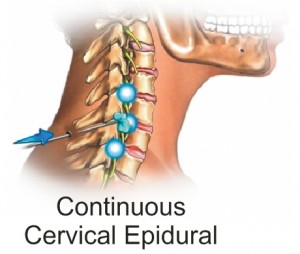
Analgesics, Muscle relaxants, Local Gel
Exercise, Physiotherapy
Local application of Hot & Cold
Interventional Pain Management:
When conservative management is not giving satisfactory outcome and there is no indication of surgical management, Interventional therapy is the best choice.
Intra-articular Steroid injection
Intra-articular Ozone therapy
PRP therapy
Intra-articular acromio-clavicular steroid injection
Continuous Suprascapular nerve block or Cervical Epidural analgesia
Injection of Subacromial Bursitis
Pulse Radio-frequency of Suprascapular nerve